Have you ever thought of something called a machine performing human activities? Probably not, but today, it is the case where machines, like computers, are replicating human intelligence. What is it called? Artificial intelligence. Then, what is artificial intelligence technology?
It is essentially about teaching computers and machines to think and act like humans. It involves enabling them to understand language, recognize patterns, solve problems, and make decisions in ways similar to ours. Let us dive deep and understand it in detail, its pros and cons, types, applications, etc.
What is artificial intelligence?
AI is like teaching machines to do tasks that humans usually do, like learning, solving problems, making decisions, and being creative. AI is like teaching machines to think and act like humans, but defining exactly what it is takes work. A recent study by PwC predicts that AI could contribute up to $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030.
At its core, AI means machines that can learn, make decisions, and take action, even in new situations they haven’t encountered before. Some people think of AI as robots with human-like intelligence and personality, but today’s Artificial Intelligence definition is far from that. It’s more about solving problems and adapting to new situations. Regular computer programs repeat the same tasks in the same way every time. They need help adapting to new situations.
AIs, on the other hand, can learn and solve more complex problems, even ones they’ve never faced before. Companies must teach computers on every road and intersection in the race to build driverless cars. Instead, they’re creating programs that can react to real-world situations using sensors, even if they’re new. We still need to have brilliant AI, like in sci-fi movies. What we have now is called weak AI or narrow AI. It’s good at specific tasks but can only do some things. So, when you hear about Artificial Intelligence, be cautious. Only some things labeled as AI are knowledgeable.
Why is artificial intelligence important?
AI rapidly transforms industries by automating repetitive tasks, freeing human time and resources. From robots handling complex assembly lines in factories to AI chatbots offering 24/7 customer service, AI streamlines operations and enhances efficiency. Beyond automation, AI excels at processing massive datasets, providing valuable insights that empower better decision-making. Businesses can utilize AI to personalize marketing campaigns, develop targeted treatments in healthcare, or predict weather patterns for environmental initiatives.
This data-driven approach fosters innovation across various fields. AI is accelerating drug discovery, aiding climate research, and even contributing to scientific breakthroughs in astronomy and genomics by analyzing vast amounts of data that might elude human observation. Generative AI tools further expand possibilities, offering applications in education, marketing, and product design. 80% of smartphone users interact with AI daily through features like voice assistants and smart recommendations.
The rise of AI isn’t just about efficiency and insights; it also creates entirely new business models. Take Uber, for example, which connects riders with taxis through a mobile app—a concept unimaginable without AI’s ability to connect users and resources in real time. Leading companies like Google, Apple, Microsoft, and Meta heavily rely on AI to power their core operations and stay competitive. AI technology is shaping the future, from Google’s search engine algorithms to self-driving cars and advancements in natural language processing.
The future of work with AI
While AI automates specific tasks, it also creates new opportunities. New roles are emerging in AI development, data analysis, and human-computer interaction. As AI meaning continues to evolve, future workers will need a combination of human skills like creativity, critical thinking, social intelligence, and a solid understanding of AI.
What are the types of artificial intelligence?
Researchers are exploring more sophisticated forms of artificial intelligence and grappling with defining intelligence and consciousness more precisely.
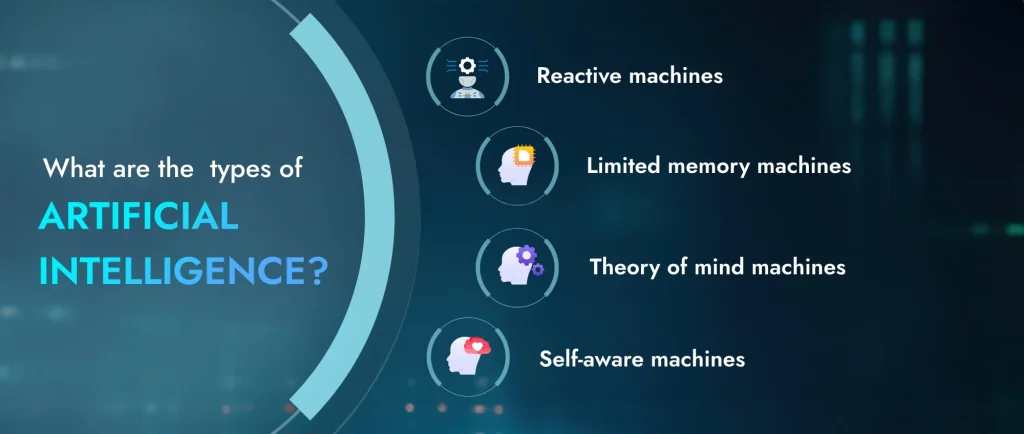
- Reactive machines: These are basic AI systems that react only to immediate stimuli, like playing chess, without any memory of past events.
- Limited memory machines: These AI systems have a limited understanding of past events, allowing them to interact more with the world, such as self-driving cars adjusting their speed based on past observations.
- Theory of mind machines: These hypothetical AI systems would understand the world and its other entities, representing an early form of artificial general intelligence.
- Self-aware machines: The most advanced type of AI, these machines would understand the world, others, and themselves, akin to achieving artificial general intelligence. However, this level of AI is currently a distant possibility.
Advantages and disadvantages of AI
People are afraid of AI, and that makes sense. There are many real concerns about it. AI has a wide range of applications that have the potential to alter the way we work and live. While many of these innovations, such as self-driving cars, virtual assistants, and wearable gadgets in healthcare, are lovely, they also present numerous concerns. It’s a complex picture that frequently evokes opposing images: utopia for some, dystopia for others. The reality is likely to be far more complex. Below, you’ll find a brief list of AI’s potential advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages of artificial intelligence
AI significantly benefits across sectors, transforming processes and improving outcomes with its capabilities. AI’s impact is expanding, driving advancement and change through increased efficiency and productivity, as well as improved decision-making and innovation.
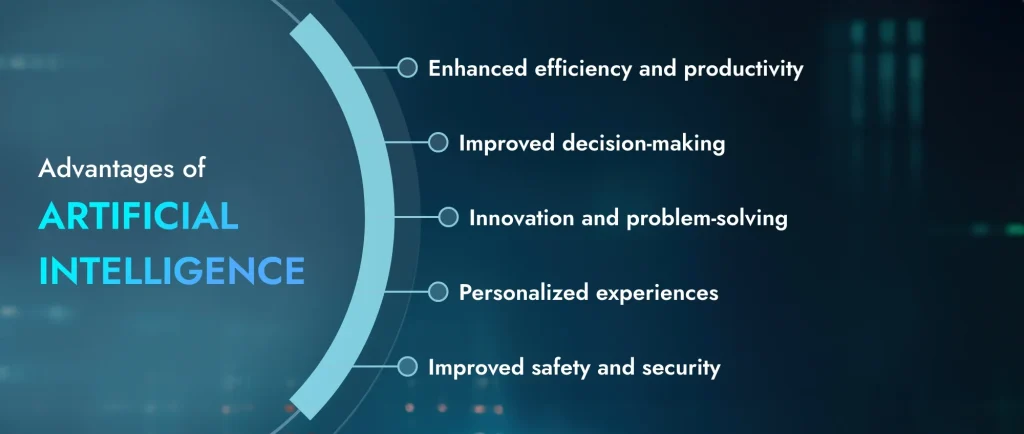
Enhanced efficiency and productivity
AI is increasingly automating repetitive tasks that were once the domain of human labor. This frees up valuable human time and resources, allowing us to focus on more strategic endeavors.
Examples:
- Manufacturing: AI-powered robots can handle complex assembly lines with greater precision and speed than humans. This increases production output, reduces errors, and improves overall efficiency.
- Customer service: AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries 24/7, freeing up human representatives for more complex issues that require a personal touch. This leads to shorter wait times and improved customer satisfaction.
Improved decision making
Traditional decision-making often relies on limited data or human intuition. AI, however, thrives on vast troves of data. AI algorithms can analyze enormous datasets, identifying hidden patterns and trends that might escape human observation. This empowers organizations to make data-driven decisions, leading to better outcomes.
Examples:
- Finance: AI can analyze financial data to identify potential risks and investment opportunities. This allows financial institutions to make more informed investment decisions and offer personalized financial advice to clients.
- Healthcare: AI can analyze medical records and imaging data to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases with greater accuracy. This can lead to earlier diagnoses and more effective treatment plans, ultimately improving patient outcomes.
Innovation and problem solving
AI has the potential to tackle complex problems that have long challenged humanity. Its ability to process vast amounts of information and identify patterns opens doors to groundbreaking innovations in diverse fields.
Examples:
- Medicine discovery: AI can analyze molecular structures to accelerate the development of new medications, leading to faster breakthroughs in the fight against diseases.
- Climate change: AI can analyze climate data and simulate potential solutions for sustainability challenges. This can help us develop more effective strategies to mitigate the effects of climate change.
Personalized experiences
AI is transforming how we interact with technology by creating personalized experiences. Recommendation systems powered by AI algorithms learn your preferences and suggest products, content, or services tailored specifically for you.
Examples:
- eCommerce: AI can analyze your purchase history and browsing behavior to recommend products you might be interested in. This personalizes the shopping experience and increases the likelihood of a purchase.
- Education: AI-powered tutoring systems can adapt to a student’s learning pace and style, providing a more personalized learning experience that caters to their strengths and weaknesses.
Improved safety and security
AI-powered systems can enhance security measures and assist in hazardous tasks, reducing risks to human safety and safeguarding valuable assets. AI technologies offer proactive solutions to various safety and security challenges using advanced algorithms and real-time data analysis.
Examples:
- Cybersecurity: AI can detect and prevent cyberattacks by analyzing network traffic patterns and identifying suspicious activity. This helps organizations protect their valuable data from cyber threats.
- Dangerous Jobs: AI-powered robots can perform hazardous tasks in industrial settings, such as handling dangerous materials or working in extreme environments. This reduces the risk of injuries to human workers.
Disadvantages of artificial intelligence
AI technologies bring numerous benefits but present several challenges and drawbacks that society must address. It will help you fully harness their potential while mitigating their negative impacts.

Job displacement
AI automates tasks, boosting efficiency but raising concerns about job displacement. Industries like manufacturing and customer service may see job losses as AI handles repetitive work. Retraining programs are crucial, focusing on skills that complement AI. Cultivating creativity, critical thinking, and social intelligence will be key for future job prospects.
Ethical considerations
AI algorithms are only as good as the data they’re trained on. Biased data can lead to biased AI systems perpetuating discrimination in areas like loan approvals, hiring practices, or facial recognition software. The potential for AI to be used for malicious purposes, such as autonomous weapons, or mass surveillance, raises ethical concerns.
It is crucial to develop ethical frameworks for AI development and deployment. This includes promoting transparency and accountability in AI algorithms, ensuring fairness, and preventing discrimination.
Explainability and transparency
Understanding how AI systems reach decisions can be complex, often shrouded in layers of algorithms and data. This lack of transparency can hinder accountability and raise concerns about potential misuse.
What if an AI-powered loan approval system only accepts loan applications with a clear explanation? This lack of transparency makes it difficult to identify and address potential biases within the system. Researchers seek ways to develop “explainable AI” systems that clearly explain their decisions. This will be crucial for building trust in AI and ensuring its responsible use.
Over reliance on AI
Dependence on AI for critical tasks without proper human oversight can pose risks. While powerful, AI systems can only sometimes handle complex situations that require nuanced human judgment and ethical considerations.
If an AI-powered stock trading algorithm makes high-risk decisions without human supervision, it could result in significant financial losses. A balanced approach is essential. Human oversight and expertise should complement AI systems, ensuring responsible decision-making and mitigating potential risks.
Existential threats
Some experts express concerns about the potential for superintelligence – AI surpassing human intelligence in all aspects. While this is a highly speculative scenario, it raises questions about the potential risks posed by AI that might not align with human values.
This is a topic of ongoing debate among AI researchers and philosophers. Some believe safeguards and ethical frameworks can prevent such risks, while others advocate for careful consideration of the long-term implications of superintelligence.
What are some examples of AI technology, and how is it used today?
Artificial intelligence used every day is already integrated into many aspects of our daily lives. Here are just a few examples of how we use AI everyday.
- Self-driving cars: Self-driving cars interpret sensor data using AI algorithms. They navigate roads autonomously. AI processes information in real-time. It makes split-second decisions to steer, accelerate, and brake. The goal is safer and more efficient transportation.
- Virtual assistants: Virtual assistants like Siri, Alexa, and Google Assistant rely on NLP and machine learning. They understand user commands and provide relevant responses. These assistants help with setting reminders, answering questions, and controlling devices. Their goal is to assist users with various activities.
- Recommendation systems: Recommendation systems analyze user data to suggest personalized content or products. Platforms like Netflix use collaborative filtering and content-based algorithms. These algorithms tailor recommendations to individual tastes. The goal is to enhance user experience and engagement.
Are you looking to apply AI in your business operations but are stuck due to a lack of time and resources for artificial intelligence? Contact us today for AI development services.
Key takeaways
- AI refers to the replication of human intelligence using machines.
- AI can potentially revolutionize various industries where human life is at risk.
- Different types of AI exist, like self-driven cars, chatbots, virtual assistance, research and development, etc.
- AI offers numerous advantages but also raises ethical and practical concerns.
- AI integration is already widespread in many technologies we use daily.
Frequently asked questions
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) is a speculative type of AI with human-level intelligence and the ability to learn and apply knowledge across various domains.
Artificial Intelligence can be broadly categorized into two main types: Narrow AI (task-specific) and Artificial General Intelligence (human-level intelligence).
Artificial Intelligence was created to automate tasks, augment human abilities, solve complex problems, and advance knowledge across various domains.
In industries, AI technology automates tasks, improves decision-making, and enhances efficiency through applications like personalized recommendations, fraud detection, and predictive maintenance.

Vishal Patel
Vishal Patel is an experienced Solution Consultant with a proven track record in the information technology and services industry.